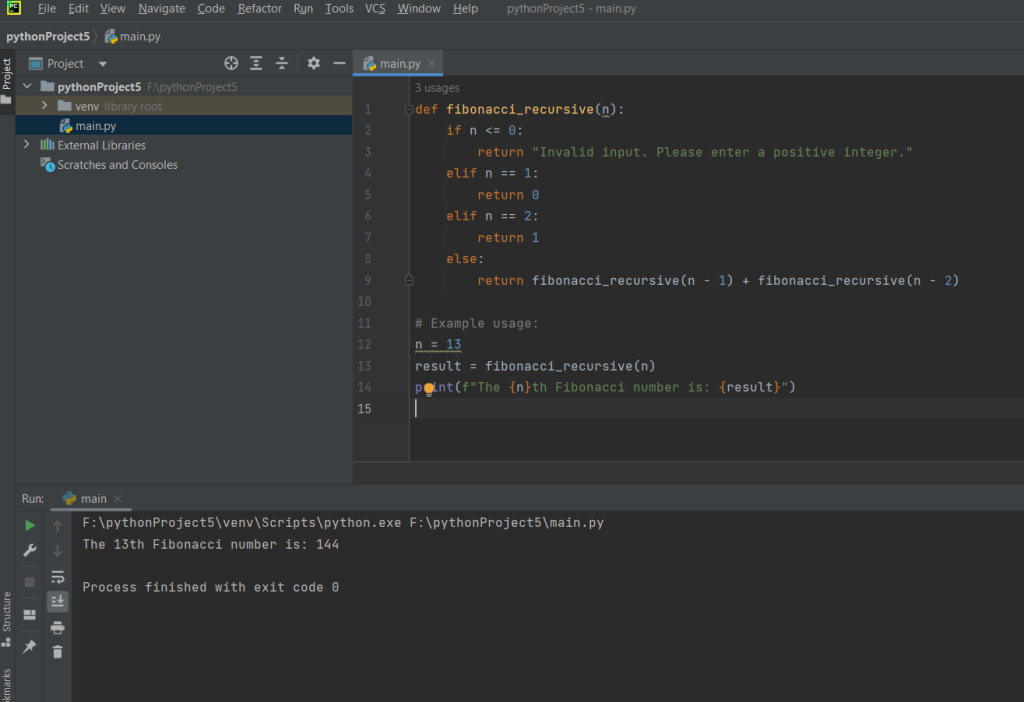
The provided Python code offers two implementations for generating Fibonacci numbers: a recursive approach and an iterative approach. In the recursive solution, the function fibonacci_recursive takes a positive integer n as input and calculates the nth Fibonacci number by recursively summing the (n-1)th and (n-2)th Fibonacci numbers. Base cases are established for n equal to 1 and 2. The iterative approach, implemented in the fibonacci_iterative function, initializes a list with the first two Fibonacci numbers and uses a while loop to iteratively compute the subsequent Fibonacci numbers until reaching the desired nth Fibonacci number. Both implementations include a check for invalid input (non-positive integers) and return an error message in such cases. The example usage demonstrates obtaining the 10th Fibonacci number using each approach. It’s worth noting that while the recursive approach is concise, it may be less efficient for large values of n due to repeated computations, making the iterative approach a more practical choice in such cases.
Source code
def fibonacci_recursive(n):
if n <= 0:
return “Invalid input. Please enter a positive integer.”
elif n == 1:
return 0
elif n == 2:
return 1
else:
return fibonacci_recursive(n – 1) + fibonacci_recursive(n – 2)
# Example usage:
n = 13
result = fibonacci_recursive(n)
print(f”The {n}th Fibonacci number is: {result}”)
Description
- Recursive Approach:
- Function Definition:
- The
fibonacci_recursivefunction is defined, taking a positive integernas its parameter.
- The
- Input Validation:
- The function checks if
nis less than or equal to 0. If so, it returns an error message indicating that the input is invalid and requests a positive integer.
- The function checks if
- Base Cases:
- If
nis 1, the function returns 0. - If
nis 2, the function returns 1.
- If
- Recursive Calculation:
- For values of
ngreater than 2, the function recursively calls itself to calculate the (n-1)th and (n-2)th Fibonacci numbers and adds them together.
- For values of
- Result:
- The final result is the nth Fibonacci number, which is returned by the function.
- Iterative Approach:
- Function Definition:
- The
fibonacci_iterativefunction is defined, taking a positive integernas its parameter.
- The
- Input Validation:
- Similar to the recursive approach, it checks if
nis less than or equal to 0, returning an error message for invalid input.
- Similar to the recursive approach, it checks if
- Initialization:
- The function initializes
fib_sequenceas a list with the first two Fibonacci numbers (0 and 1).
- The function initializes
- Iterative Calculation:
- A
whileloop is used to iteratively calculate and extend the Fibonacci sequence until its length reachesn. At each step, the next Fibonacci number is computed as the sum of the last two numbers in the sequence.
- A
- Result:
- The nth Fibonacci number is returned as the result of the function.
Screenshot