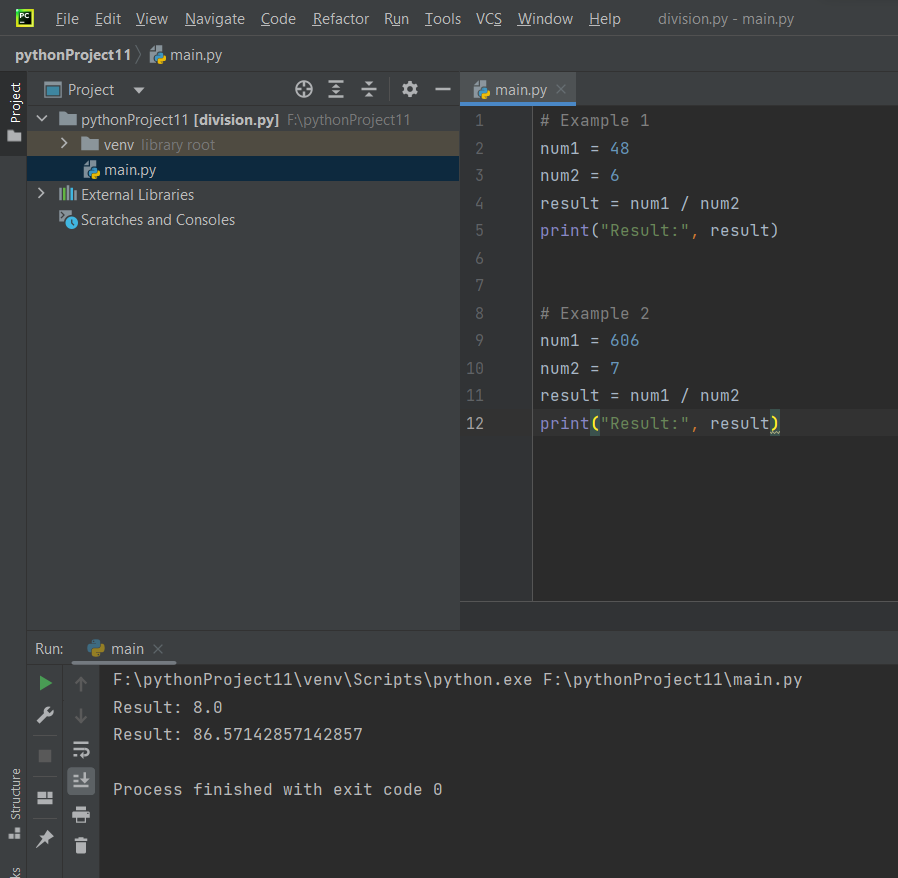
The provided Python code consists of two examples showcasing division operations. In the first example, two variables, num1 and num2, are assigned the values 48 and 6 respectively. The code then utilizes the division operator (/) to divide the value in num1 by the value in num2. The result of this operation, which is 8.0, is stored in a variable named result. Subsequently, the code prints the result using a print statement.
The second example follows a similar structure, with num1 assigned the value 606 and num2 assigned 7. The division operation is again employed to calculate the quotient of num1 divided by num2, resulting in approximately 86.57142857142857. This result is stored in the variable result, and the code prints it out using the print statement.
In summary, both examples demonstrate the basic use of the division operator in Python to compute the quotient of two numbers, and the results are printed for clarity. The division operation in Python produces floating-point results, accommodating both integer and non-integer division scenarios.
Source code
# Example 1
num1 = 48
num2 = 6
result = num1 / num2
print("Result:", result)
# Example 2
num1 = 606
num2 = 7
result = num1 / num2
print("Result:", result)Description
Example 1:
- Variable Assignment: Two variables,
num1andnum2, are assigned numerical values (48and6, respectively).num1 = 48 num2 = 6 - Division Operation: The
/operator is used to divide the value stored innum1by the value innum2. The result,8.0, is assigned to a variable namedresult.result = num1 / num2 - Print Result: The code then prints the result of the division.
print("Result:", result)This line outputs: “Result: 8.0”.
Example 2:
- Variable Assignment: Two variables,
num1andnum2, are assigned numerical values (606and7, respectively).num1 = 606 num2 = 7 - Division Operation: The
/operator is used again to divide the value stored innum1by the value innum2. The result, approximately86.57142857142857, is assigned to a variable namedresult.result = num1 / num2 - Print Result: The code then prints the result of the division.
print("Result:", result)This line outputs something like: “Result: 86.57142857142857”.
These examples demonstrate the step-by-step process of assigning values, performing division operations, storing results, and printing the output in Python. The division operation in Python produces floating-point results, reflecting the precision of the calculation.
Screenshot